Roman SKOKOV
Professor of the Department of Management
and Logistics at the Agroindustrial Complex of the
Volgograd State Agrarian University, Director of the
Volgograd Center for Science and Technology –
a branch of the Federal State Budgetary Institution «REA»
of the Ministry of Energy of Russia, Doctor of Economics
e-mail: rskokov@mail.ru
Alexander FETISOV
Director of VPI (branch) VolgSTU, Ph.D., associate professor
e-mail: fetisov@vstu.ru
Viktor KRIVKO
Deputy Head of the Production and Dispatch Service
of Gazprom Transgaz Volgograd LLC,
Candidate of Agricultural Sciences
e-mail: vnkrivko@yandex.ru
At the present stage, the main type of fuel for generating thermal energy is natural gas supplied through a gas pipeline. Its share in the consumption of energy facilities is about 80% [2].
The uninterrupted supply of this fuel to boiler plants, as practice shows, depends directly on the reliability of each element included in the fuel supply system [1].
It is obvious that the construction of additional gas pipelines is a laborious and time-consuming process that requires huge financial costs. To minimize them, reserve fuel facilities are provided. Reserve fuel facilities – a set of equipment and devices designed for storage, supply and use of reserve (emergency) fuel.
In domestic legislation, the maintenance of good condition and safe operation of power equipment is provided by supervisory authorities [5]. Over the previous years of reforming, there was a serious weakening of control over compliance with the requirements of standards for providing heat sources with reserve fuel [3]. The problems with the continuation of a number of functions by the authorities emerged.
However, the regulatory and legal documentation retains the mandatory requirements for providing heat sources with reserve and emergency fuel in case of emergency situations, since the heat supply to consumers should not be disrupted, and the heat supply company should not incur losses from the costs of eliminating emergencies and from failure to fulfil its obligations to ensure consumers of thermal energy in the required volume.
Currently, the institute of reserve fuel economy is based on the following regulatory and legal framework:
- Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 162 “On Approval of the Rules for Gas Supply in the Russian Federation” dated February 5, 1998.
- Instructions on the enterprise gas consumption reservation formalization and the schedules for switching consumers to reserve types of fuel in case of cold snaps, approved by the head of the Department of State Energy Supervision and Energy Saving of the Ministry of Fuel and Energy of Russia dated June 11, 2000.
- Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 317 “On Approval of the Rules for the Use of Gas and the Provision of Gas Supply Services in the Russian Federation” dated May 17, 2002.
- Order of the Ministry of Energy of Russia No. 448 “On the Approval of Regulations Necessary for the Implementation of the Rules for the Use of Gas and the Provision of Gas Supply Services” dated December 16, 2002.
- Order of the Ministry of Energy of the Russian Federation of March 24, 2003 No. 115 “On Approval of the Rules for the Technical Operation of Thermal Power Plants.”
ENERGY
Pursuant to Art. 4 of the Federal Law No. 69-FZ “On Gas Supply in the Russian Federation” dated 31.03.1999, one of the principles of the state policy in the field of gas supply in Russia is the state regulation of the rational use of gas reserves and ensuring the energy security of the Russian Federation.
In accordance with the legislation, thermal power plants for starting gas must ensure the operability of the reserve fuel economy and the readiness of gas-using equipment to operate on reserve fuel, as well as create fuel reserves in accordance with the standards.
The procedure for supplying consumers with gas during periods of cold snaps and in case of emergency situations on gas transmission systems is established by the Ministry of Energy of Russia.
The executive authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation approve the schedules for switching consumers to reserve types of fuel in the event of a cold snap and the procedure for putting these schedules into effect, as well as schedules for limiting the supply of gas to buyers and the sequence of their shutdown in the event of a disruption of the technological mode of operation of the gas transmission system in an accident.
Ensuring gas supplies to public utilities and the population during periods of cold snaps with maximum gas withdrawals from the gas transmission system can be performed by transferring a number of consumers to reserve types of fuel. The volumes of released gas resources for these purposes are determined by the schedules for the transfer of organizations to reserve types of fuel in case of cold snaps. Transition schedules are developed by regional gas companies, the Mezhregiongaz branches, gas transportation organizations, gas distribution organizations, coordinated by the state energy supervision authorities and approved by the executive authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation separately for the first and fourth quarters.
The gas consumption pre-order amount is also calculated and signed by the representative of the state energy supervision body in the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and the head of the gas consumer organization. The gas consumption reservation is the minimum volume of gas consumption required for accident-free, subject to the maximum use of reserve fuels, the operation of technological equipment of buyers, gas supplies to which, in accordance with laws and other regulatory legal acts, cannot be terminated or reduced below a certain limit.
In order to fulfil the powers in the field of reserve fuel economy in December 2004, the RF Ministry of Energy established federal state institutions – the Directorates for Energy Efficiency and Energy Saving on the basis of gas and oil inspections of the State Energy Supervision Authority. The Energy Efficiency and Energy Saving Departments were included in the list of organizations subordinate to the Ministry of Energy. In 2015, in accordance with the order of the Ministry of Energy of the Russian Federation No. 605 dated 15.12.2011, they were reorganized by joining the Federal State Budgetary Institution “Russian Energy Agency” of the Ministry of Energy of Russia, the charter of which included the types of activities related to the reserve fuel economy, calculation of gas consumption preordering.
The main subjects of activity in the field of reserve fuel economy are (Fig. 1): Government of the Russian Federation, Ministry of Energy of the Russian Federation, executive authorities of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation, PJSC Gazprom, LLC Gazprom Mezhregiongaz, branches of LLC Mezhregiongaz, FSBI Russian Energy Agency, Ministry of Energy of Russia and its branches in constituent entities of the Russian Federation, Rostekhnadzor and its Technical Department, organizations-consumers of gas.
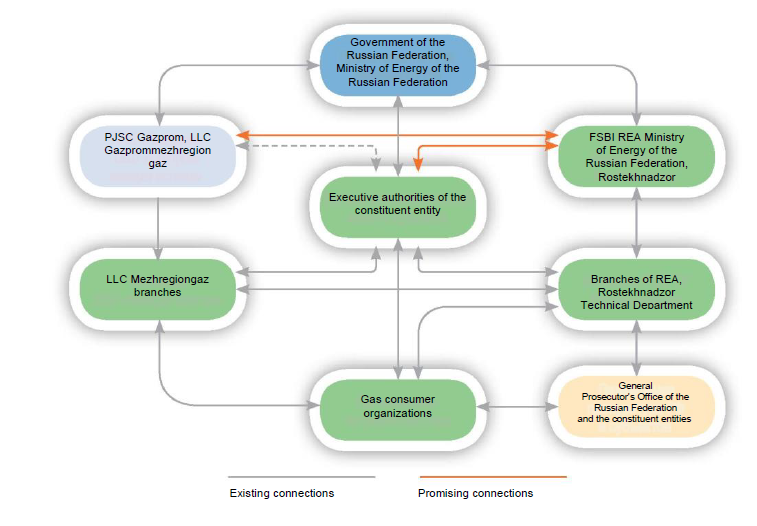
The issue of annual preparation of reserve fuel facilities for the autumn-winter period is under the control of the Gazprom management and the RF Prime Minister.
The Ministry of Energy, under the leadership of N.G. Shulginov, considers the issue of methods for monitoring the technical condition of reserve fuel facilities of electric power entities, including amendments to the legislation regarding the collection of information necessary for this monitoring [4].
The urgency of the problems of the institute of reserve fuel economy is due to a number of reasons:
- The low level of operability of the reserve fuel economy and reserve fuel reserves at the present stage creates risks for Gazprom and the executive authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
- The improper state of the reserve fuel economy and the lack of the necessary reserves of reserve fuel, in the event of an emergency on the gas pipeline, will lead to a halt in the work of organizations, negative social consequences if the organization is a social facility (hospital, school, maternity hospital, etc.) and significant economic damage to commercial enterprises , especially in production with a continuous cycle.
- Decrease in the effectiveness of the authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation exercising their powers to draw up schedules for the transfer of organizations to reserve types of fuel in case of cold snaps (clause 19 of the Government Decree No. 162 dated 05.02.1998).
In the process of designing heat supply systems for industrial enterprises and other energy facilities, the most important issue is the reliability of fuel supply to the facility. Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 679 dated 08.08.2013 cancelled the previously obligatory permits for the start of gas extraction for the use of gas as a fuel, the so-called “gas limits” or the fuel regime. Fuel mode is a permit issued in accordance with the established procedure and granting the right to use any fuel as a reserve or main one. Therefore, according to the updated version of the Rules for the use of gas and the provision of gas supply services in the Russian Federation, the construction of a reserve fuel economy and the creation of fuel reserves should include a gas supply project.
However, in recent years, when designing power facilities, customers, in order to save on capital costs during construction, try not to invest in a backup fuel supply system. At the present stage, in the field of reserve fuel economy, a situation has developed when the reserve fuel facilities envisaged by the projects to provide reserve fuel for boiler houses were either mothballed, or did not function due to equipment malfunction, or were completely eliminated.
Investments in maintaining and renewing the reserve fuel economy at a low level.
In the Volgograd Region, according to the fuel regimes issued in previous years, 105 organizations were included in the schedules for the transfer of organizations to reserve types of fuel during cold snaps, of which in 2020 only 62 (59%) conducted an independent survey of readiness to operate on a reserve type of fuel, 38 (36 %) refused to be examined and 5 (5%) conducted self-examination.
In the Astrakhan region, 12 organizations were included in the transition schedules, of which in 2020 6 (50%) conducted an independent survey of readiness to operate on a reserve type of fuel, 5 (42%) refused the survey, 1 (8%) conducted a self-examination.
This situation in the field of reserve fuel supply to boiler houses is typical for many regions of Russia.
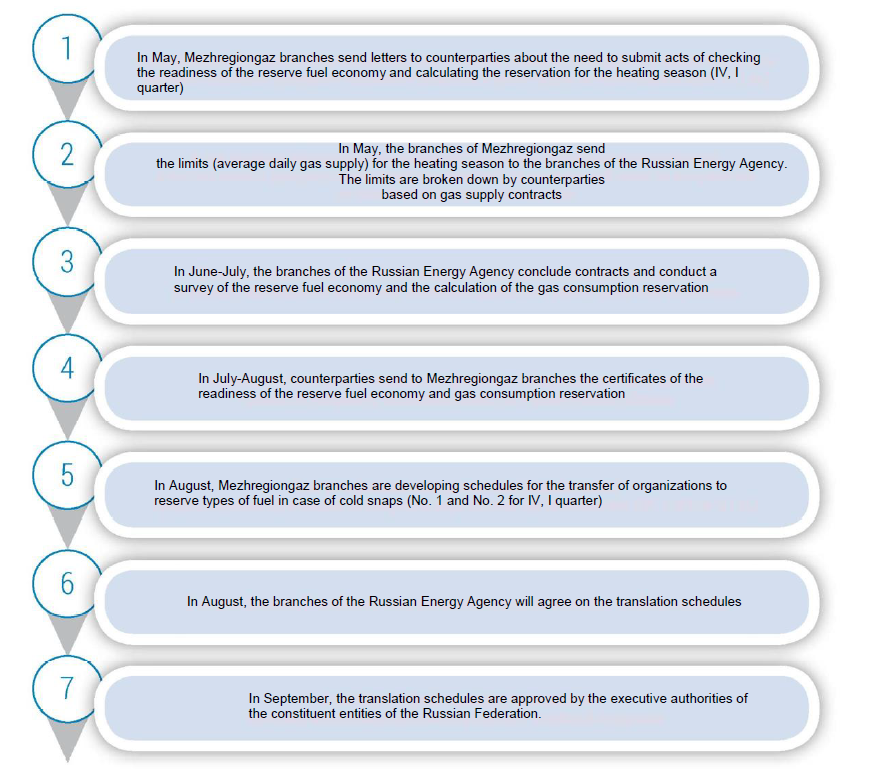
To organize systematic work in the field of reserve fuel economy, the following algorithm of functioning of the institute of reserve fuel economy in the constituent entities of the Russian Federation is proposed (Fig. 2).
The factors that reduce the efficiency of this algorithm are:
- Cancellation of item 5 of Government Decree No. 317 stating that supervision over the rational and efficient use of gas is performed by the Ministry of Energy of the Russian Federation, represented by its authorized state energy supervision units (Government Decree No. 727 dated 19.06.2017).
- Cancellation of the fuel regime (Government Decree No. 679 dated 08.08.2013).
- The absence in the Order of the Ministry of Energy of the Russian Federation dated December 16, 2002 No. 448 of a direct reference to the obligation to agree on the transfer schedules by the branches of the Russian Energy Agency (clause 1 in the modern edition – “approved by the state energy supervision authorities”).
- The lack of a clear position on the part of the executive authorities of a number of entities, branches of Gazprom Mezhregiongaz on the issue of self-examination and examination of the readiness of the reserve fuel economy and the calculation of the amounts preordered by the non-governmental organizations.
To discuss the problems of the reserve fuel economy institute, on April 22, 2021, the Volgograd Centre for Science and Technology, a branch of the Ministry of Energy of Russia, held the 1st All-Russian webinar “Reserve fuel economy and gas consumption reservation in the 2021–2022 heating season”.
Following proposals were developed to improve the efficiency of the functioning of the institute of reserve fuel economy in modern conditions in the course of the seminar:
- Amend the order of the Ministry of Energy of the Russian Federation of December 16, 2002 No. 448, securing the obligation to agree on the transfer schedules with the REA of the Ministry of Energy of Russia. REA is a budgetary scientific institution. It has a wide regional network of 62 branches covering 85 constituent entities of the Russian Federation. The branches have the necessary material and technical base, have qualified specialists, an archive of fuel modes, extensive experience in performing work on the examination of the possibility of operation of gas-using equipment on a reserve type of fuel, the state of reserve fuel facilities, calculation and registration of gas consumption pre-order amounts.
- REA shall sign cooperation agreements on this issue with Gazprom or Gazprom Mezhregiongaz. Public-private partnership will enable the more efficient development of the reserve fuel economy institute, as well as the scientific cooperation in the field of energy in many areas.
- When designing new gas consumption facilities, provide for the construction of a reserve fuel economy and the creation of fuel reserves. In the technical conditions for connection to the gas distribution network, issued by the gas distribution organization, provide for the reserve fuel facility.







